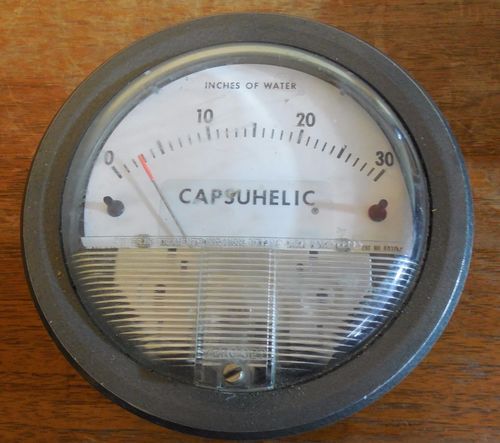
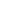
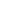
Dwyer 4005 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gauge
Dwyer 4005 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gauge Specification
- Grade
- Industrial
- Thread
- 1/8 NPT Female
- Seal Material
- Silicone rubber
- Display
- Analog
- Sensor Type
- Diaphragm, Differential Pressure
- Outer Size
- 4 inches (102 mm) diameter
- Material
- Die-cast aluminum case, acrylic cover
- Dial Material
- Aluminum
- Pointer Material
- Anodized aluminum
- Processing Type
- Machined
- Diameter
- 4 inches
- Glass Size
- 4 inches
- Mount Type
- Panel Mount
- Scale Range
- 0-5 Inches Water Column (WC)
- Accuracy
- 2% of full scale
- Finishing
- Clear plastic front, painted aluminum casing
- Measure Pressure Of
- Air and non-corrosive gases
- Accessories
- Mounting ring, dust plug, screws
Dwyer 4005 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gauge Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 12 Pieces
- Payment Terms
- Cash on Delivery (COD), Paypal, Cash Against Delivery (CAD), Telegraphic Transfer (T/T), Cash in Advance (CID), Cheque, Cash Advance (CA)
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Main Export Market(s)
- Australia, South America, Middle East, Western Europe, Central America, Asia, Eastern Europe, North America, Africa
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Dwyer 4005 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gauge
Dwyer 4005 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gauge
Dwyer Instruments 4005
Capsuhelic Differential Press. Gauge, 0-5 in H2O, brass case
Differential Pressure Gage, Range 0-5.0" w.c., For Vertical Scale Position Only.
The Capsuhelic gauge is designed to give fast, accurate indication of differential pressures. The gauge may be used as a readout device when measuring flowing fluids, pressure drop across filters, liquid levels in storage tanks and many other applications involving pressure, vacuum or differential pressure. Using the basic design of Dwyer's time-proven Magnehelic gauge, the Capsuhelic gauge contains a simple, frictionless movement that permits full scale readings as low as 0.5 in H2O. The pressure being measured is held within a capsule which is an integral part of the gauge. This containment of the pressure permits the use of the gauge on system pressures of up to 500 psig, even when differentials to be read are less than 0.1 in H2O. The diaphragm-actuated Capsuhelic gauge requires no filling liquid which might limit its outdoor applications. Zero and range adjustments are made from outside the gauge, and there is no need to disassemble the gauge in normal service. Note: May be used with Hydrogen. Order a Buna-N diaphragm. Pressures must be less than 35 psi.
Product Highlights
Brass case
0-5 in H2O
Reliable Differential Pressure Monitoring
The Dwyer 4005 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gauge stands out for its industrial-grade precision and reliability. It uses a diaphragm sensor with an analog display to provide clear and accurate readings, making it ideal for HVAC systems, filter monitoring, and cleanroom applications. The unit is intended for use with air and other non-corrosive gases, ensuring compatibility with a broad range of facilities.
Durable Construction & Easy Installation
Constructed with a die-cast aluminum case and a clear, impact-resistant acrylic cover, the Dwyer 4005 is built to withstand harsh environments. Its panel mount design, accompanied by mounting accessories such as a ring, dust plug, and screws, ensures straightforward integration into control panels. The instruments external zero adjustment screw allows for quick and simple recalibration when needed.
FAQs of Dwyer 4005 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gauge:
Q: How do I install the Dwyer 4005 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gauge?
A: The gauge is designed for vertical panel mounting. Use the supplied mounting ring, screws, and dust plug to securely fix the gauge with its 4-inch diameter face. Connect the high and low pressure ports using 1/8 NPT female threads to the respective process lines for accurate differential measurement.Q: What media can be measured with this pressure gauge?
A: The Dwyer 4005 Capsuhelic is suitable for measuring the differential pressure of air and other non-corrosive gases. Avoid using it with corrosive gases, liquids, or particulates to maintain its integrity and accuracy.Q: When should I perform zero adjustment on the gauge?
A: Zero adjustment should be performed when you notice the pointer deviating from zero with no pressure applied or after installation. Use the external zero adjustment screw to recalibrate, ensuring precise readings each time.Q: Where can the Dwyer 4005 Capsuhelic be used effectively?
A: This gauge is effective in industrial settings such as HVAC monitoring, cleanrooms, filter status monitoring, and laboratory environments where monitoring low differential pressures of air and non-corrosive gases is essential.Q: What are the key benefits of using this differential pressure gauge?
A: Users benefit from its high measurement accuracy (2% of full scale), robust build, easy installation, and straightforward analog readout. The NEMA 1 equivalent enclosure and durable materials ensure reliable operation in demanding industrial settings.Q: How do I maintain or clean the Dwyer 4005 gauge?
A: Maintain the gauge by keeping the acrylic cover clean and ensuring the ports remain free from contaminants. Periodically verify calibration using the external zero adjustment, and avoid exposing the device to corrosive substances or exceeding its pressure and temperature limits.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Series 4000 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gage Category
Dwyer 4020 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gauge
Price 9871034100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 12 Pieces
Accuracy : 2% of Full Scale
Seal Material : Silicone Rubber
Display : Analog Gauge
Scale Range : 010 in H2O
Dwyer 4030 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gauge
Price 9871034100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 12 Pieces
Accuracy : 2% of full scale
Seal Material : Silicone rubber gaskets
Display : Analog
Scale Range : 030 inches of water gauge (inH2O)
Dwyer 4060 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gauge
Price 9871034100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 12 Pieces
Accuracy : 2% of Full Scale
Seal Material : BunaN
Display : Analog
Scale Range : 060 inches H2O (various ranges available)
Dwyer 4004 Capsuhelic Differential Pressure Gauge
Minimum Order Quantity : 12 Pieces
Accuracy : 2% of Full Scale
Seal Material : BunaN
Display : Analog
Scale Range : 04 in. H2O (Inches of Water)

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry